

peledina declined including in lakes Onega and Ladoga due to a reduction in its obligate hosts and eutrophication in reservoirs. In the second half of the 20th century, the abundance and habitat area of A. Therefore, despite a wide area, the acanthobdellids are classified as rare species and listed as endangered in Buryatia and the Irkutsk Region. Since acanthobdellids have a relatively low frequency of occurrence, it is obvious that their total number in distinct populations of the Siberian reservoirs is very low. peledina is more stenoecic than fishes, which it infests. Its area of distribution is much smaller compared with that of their hosts-Salmonidae and Thymallidae. Acanthobdella peledina is psychrophilic and stenoecic species inhabiting oligotrophic waters exclusively. peledina has a wide range of habitat at high latitudes of the Northern Palearctic-from Norway on the west to the Kolyma Region on the east and in North America. livanowi (Epstein, 1966), which has a limited range in fresh waters of Kamchatka and Chukotka Peninsulas and a poorly studied biology, A. These archaic freshwater leech-like clitellates belonging to Acanthobdellida are semipermanent parasites, restricted almost exclusively to salmonoid fish.

peledina in fact occupies a transitional phylogenetic position between the oligochaetes and the leeches, as shown by morphological and life cycle investigations and molecular phylogenetic analyses.

#Life leech 3.1 review series#
A series of investigations has corroborated Livanow’s phylogenetic hypothesis. peledina goes back to Livanow’s monograph of 1905 that was updated by the author in his publication in 1931 in which this species was identified as an ancient hirudinean and close phylogenetic relationships between both the Hirudinea as well as the Oligochaeta were proposed. Our basic knowledge of morphology of the A. The continued scientific interest in the Acanthobdellida is due to its mosaic combination of oligochaetous and hirudinean characters (leeches with setae), suggesting their intermediate role between Oligochaeta and Euhirudinea.Īcanthobdella peledina (Grube, 1851) is one of two known species of this group. The Acanthobdellida, a group of annelid worms, comprises of parasites of fish, which are restricted to the extreme northern parts of the northern hemisphere. Biology and lifestyle of the parasite population are revealed for the first time. peledina from other water systems of Eurasia. The ratio of body length to width in studied acanthobdellid collection is significantly less than one provided for the A.
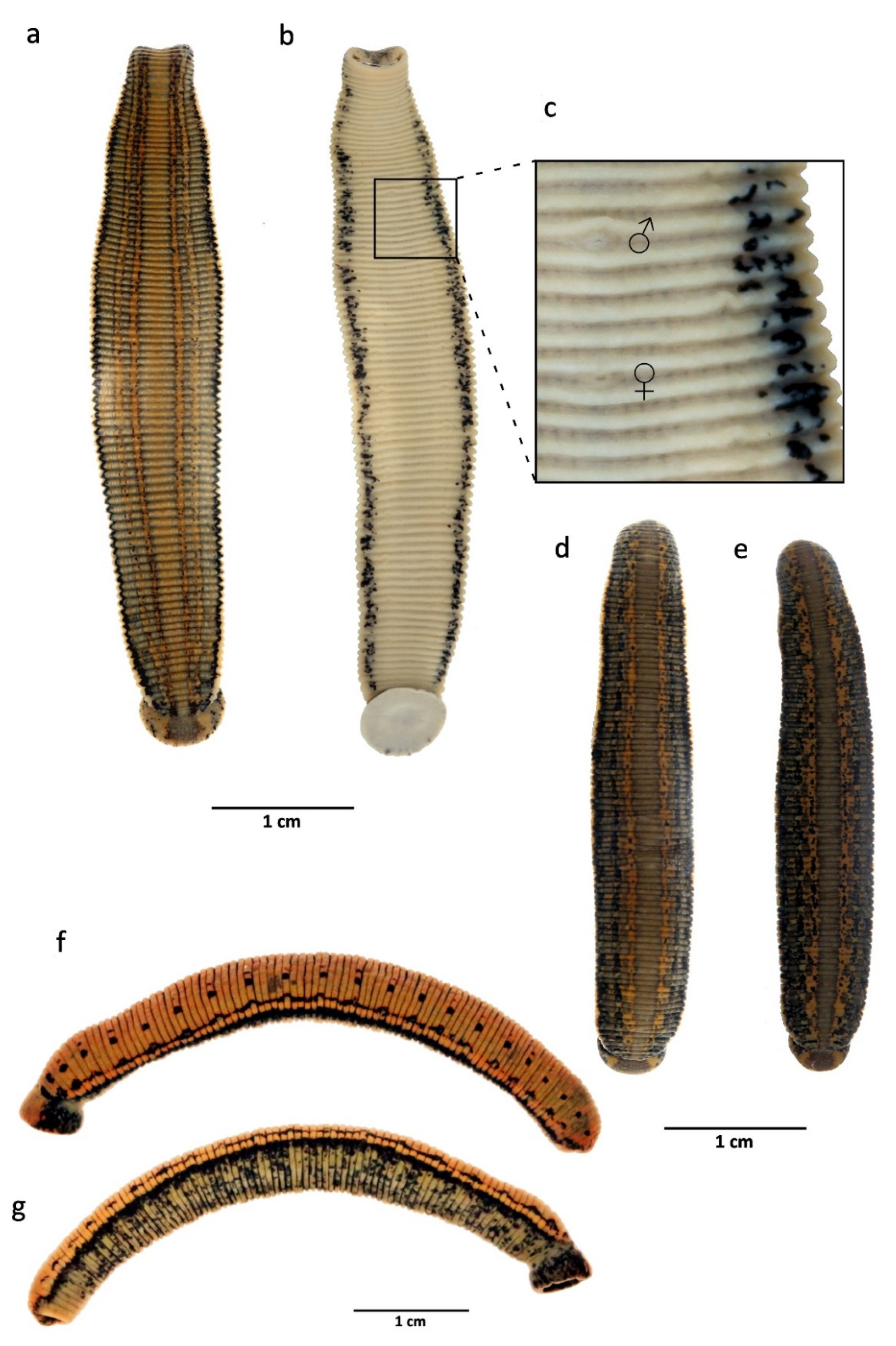
New and more specific data on morphological peculiarities and feeding strategy were obtained. In this paper, we report on the mass affection (up to 70.7%) of fish in lower course of the Chechuj River, a right tributary of the Lena and provide information on finding Acanthobdella peledina on two of six salmonoid fish species inhabiting there: lenok and grayling. Although Acanthobdella species have been known to infect several threatened species in Eurasia, little is known about their ecology and epidemiology. Salmonoid fish bdellosis is caused by leech-like ectoparasites in the monogenetic order Acanthobdellida.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
